% Код для сглаживания
function [ yy_smooth ] = kernel_smoother( xx, yy, xx_smooth, h )
yy_smooth(1:numel(xx_smooth)) = nan;
kernel = @(x0,x) exp(-(x0-x).^2 / 0.5 / h^2);
n = numel(yy);
% Evaluating yy_smooth
function yhat = y(x0)
numerator = 0;
denominator = 0;
for i = 1:n
ker_x0xi = kernel(x0,xx(i))*yy(i);
numerator = numerator + (ker_x0xi * yy(i));
denominator = denominator + ker_x0xi;
end
yhat = numerator/denominator;
end
% Filling yy_smooth vector
for j = 1:numel(xx_smooth)
yy_smooth(j) = y(xx_smooth(j));
end
end
% --------------------------
% Код для прогнозирования
% 'p' -- порядок регрессионной зависимости, т.е. сколько предыдущих значений используется для прогноза
function [ yy_forecast ] = kernel_forecaster( xx, yy, xx_forecast, h, p )
yy_forecast = [];
for xi = xx_forecast
xx = xx((end-p):end);
yy = yy((end-p):end);
yy_forecast = [...
yy_forecast, ...
kernel_smoother(xx,yy,xi,h)];
xx = [xx, xi];
yy = [yy, yy_forecast(end)];
end
end
% --------------------------
%Само использование
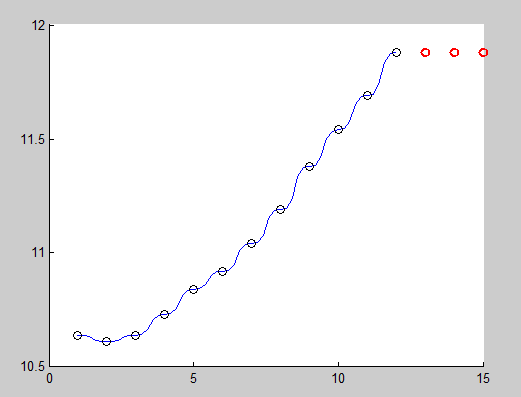
y = [10.64 10.61 10.64 10.73 10.84 10.92 11.04 11.19 11.38 11.54 11.69 11.88];
x = 1:numel(y);
xx_smoothed = 1:0.2:numel(y);
xx_forecast = x(end)+1:1:x(end)+3;
yy_smoothed = kernel_smoother(x, y, xx_smoothed, 0.7);
yy_forecast = kernel_forecaster(x,y,xx_forecast, 0.7, 4);
%Дальше идет простая визуализация