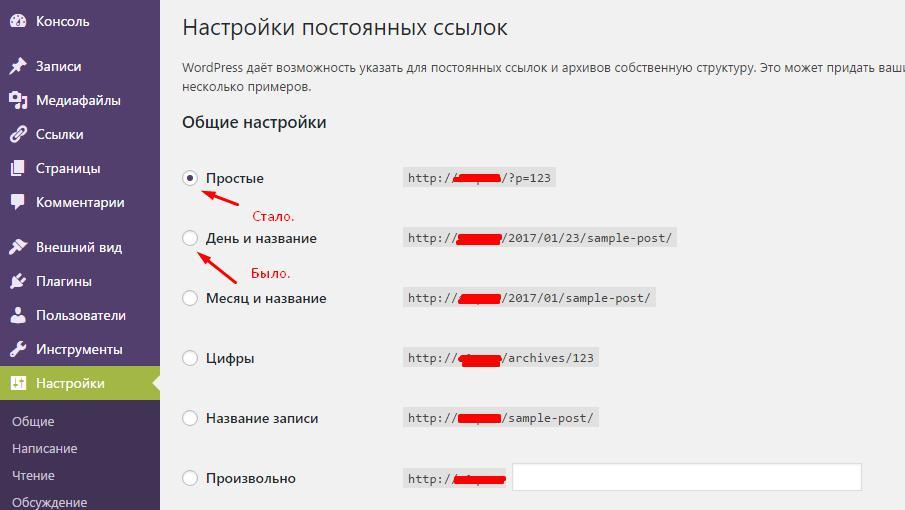
Есть 2 различные директории с разными файлами .htaccess в каждой:
.htaccess №1:
# BEGIN [SEO_REDIRECTION]
ErrorDocument 404 /index.php?error=404
# END [SEO_REDIRECTION]
# BEGIN WordPress
<IfModule mod_rewrite.c>
RewriteEngine On
RewriteBase /
RewriteRule ^index\.php$ - [L]
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteRule . /index.php [L]
</IfModule>
# END WordPress
.htaccess №2:
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f
RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d
RewriteCond $1 !^(redirect\.php)
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ redirect.php?l=$1 [L]
Появилась необходимость объединить их в одну, но если я просто "склеиваю" содержимое .htaccess, то ничего не работает. Я пробовал убирать различные строки, но ничего не выходило все равно. Прошу прощения за кривой код, я нуб.